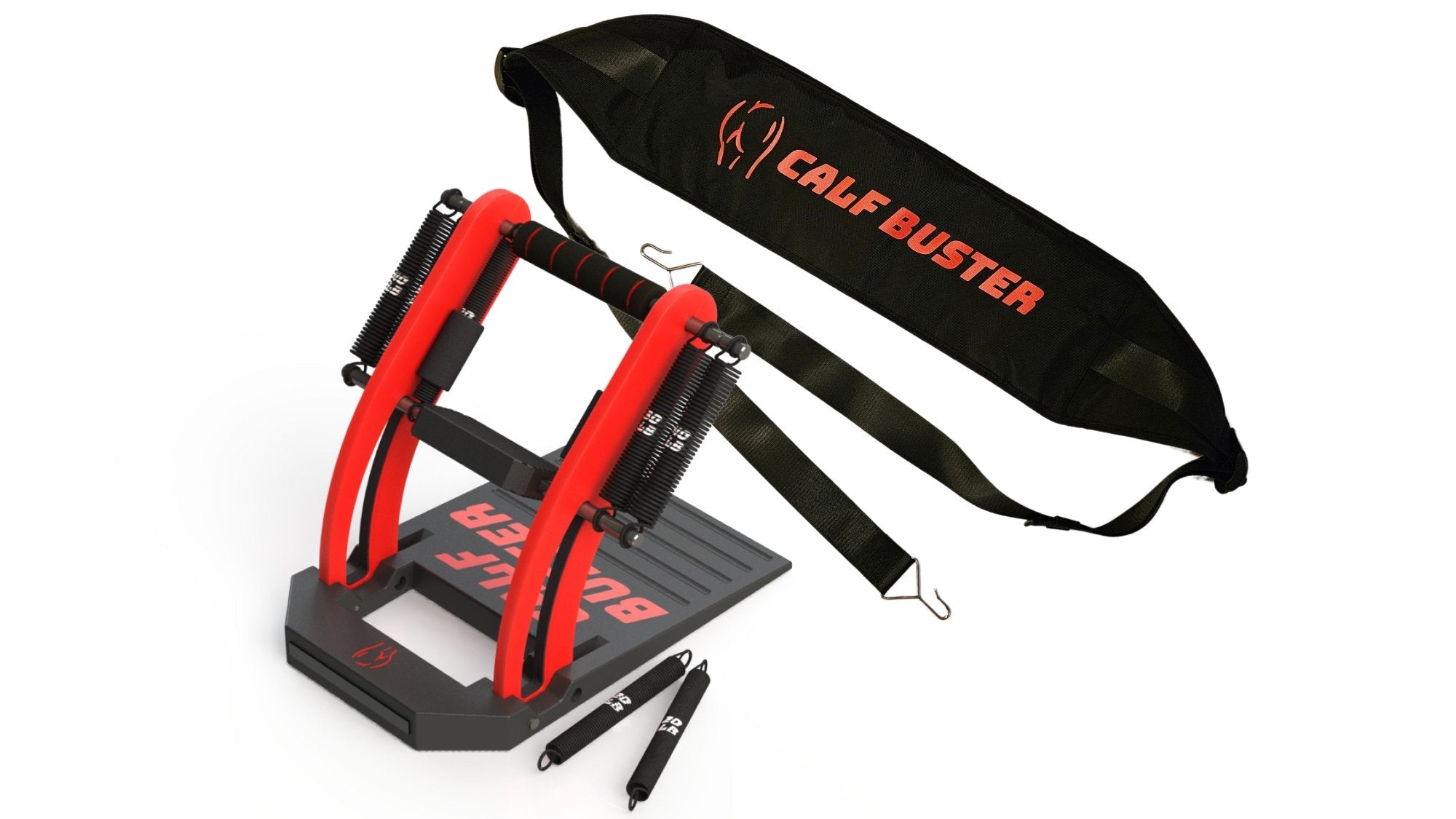
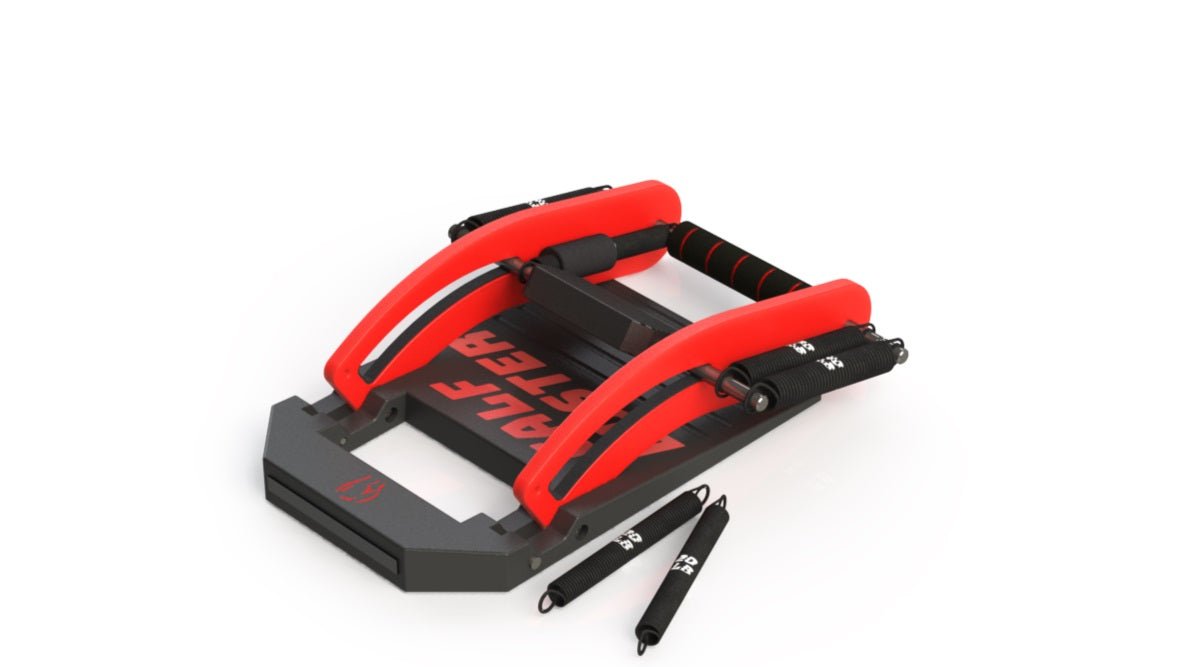
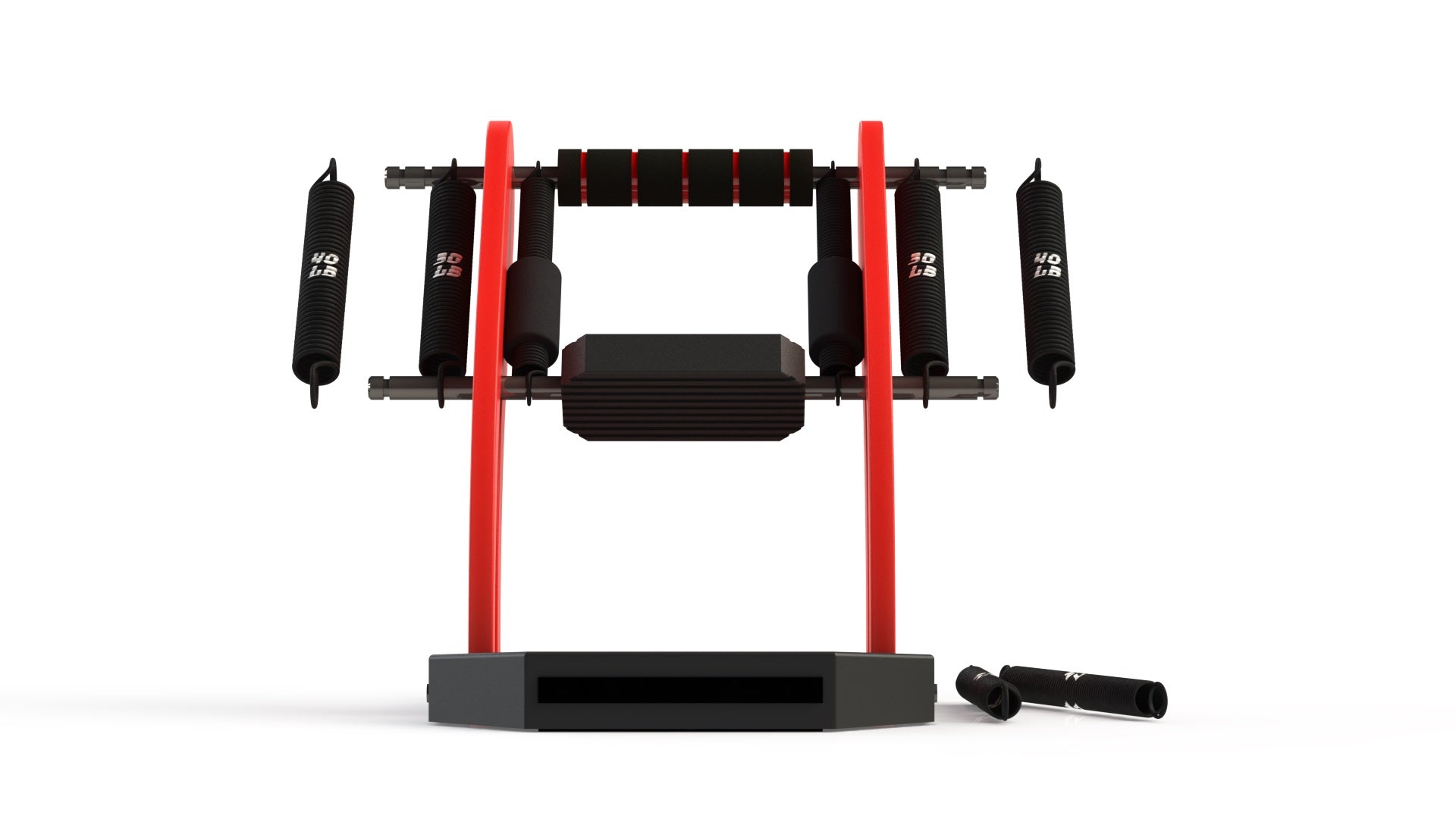
Performance Training & Injury Recovery
Ankle Strength & Jumping Power
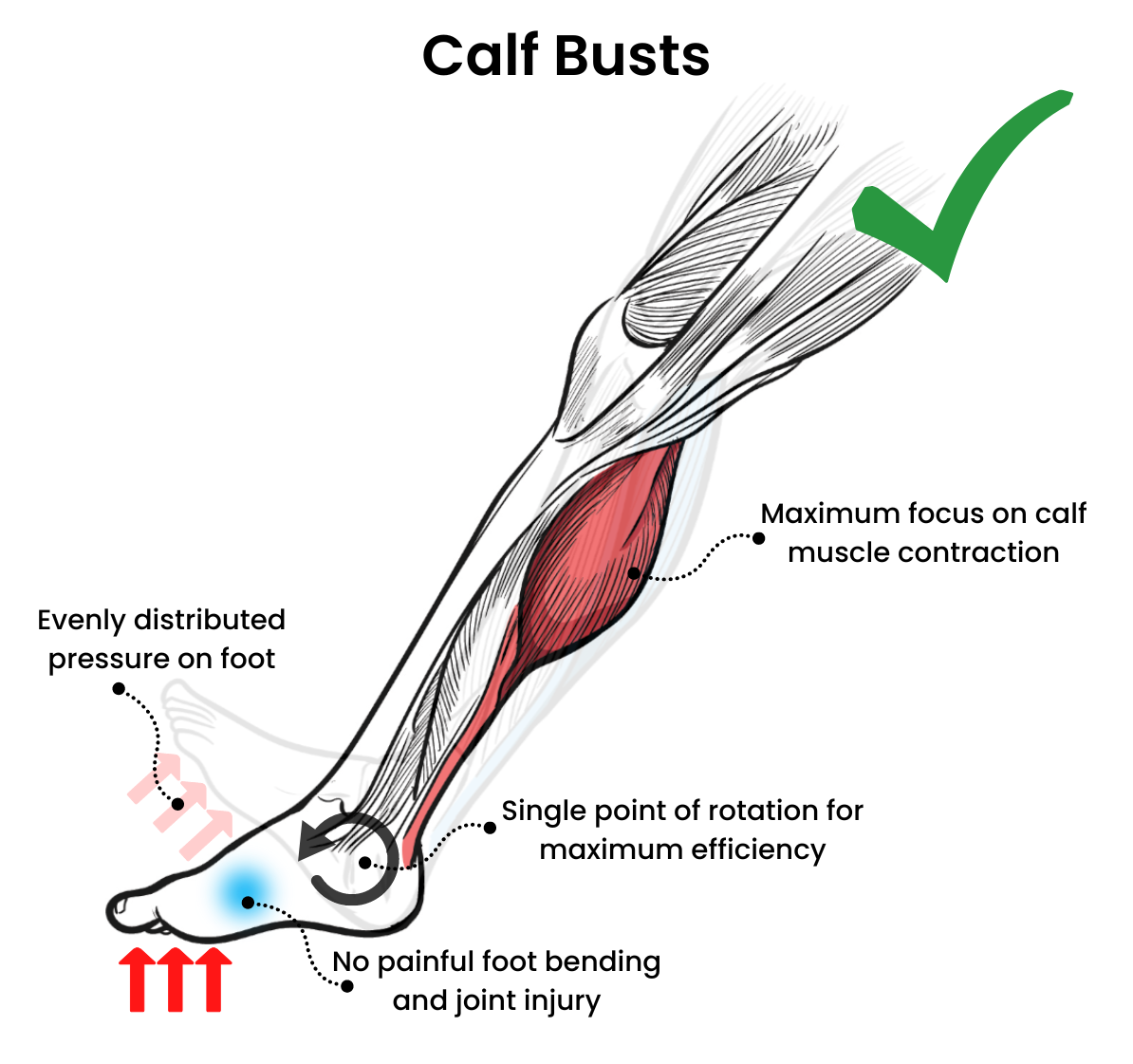
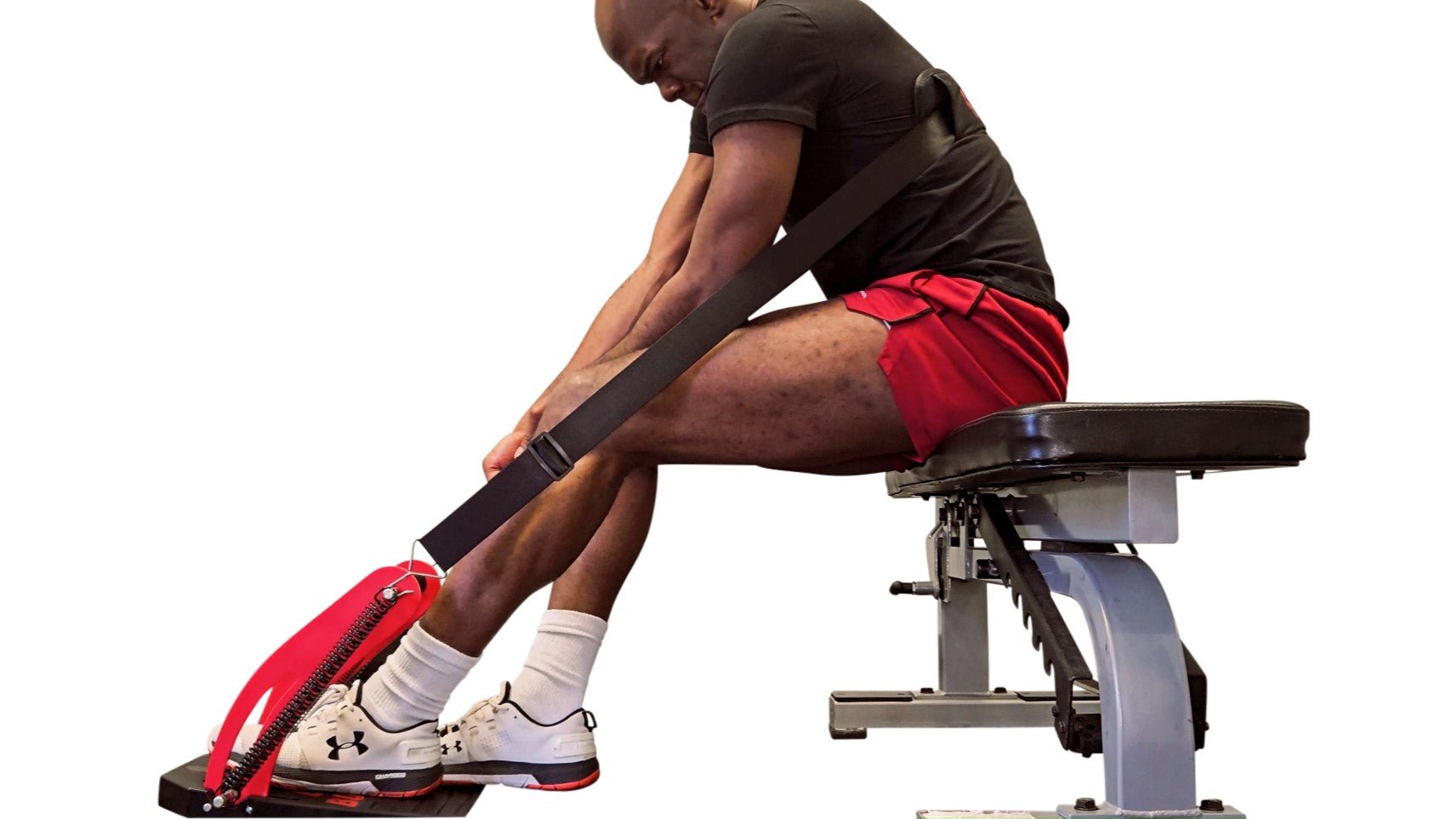
Calf training is an essential component of building jumping power and preventing ankle injuries due to the biomechanical role of the calf muscles during jumping movements. The calf muscles, which include the gastrocnemius and soleus, are responsible for plantarflexion, the movement that points the foot downward. During a jump, these muscles contract concentrically to generate force and propel the body upward.
When the calf muscles are strengthened, the gastrocnemius, with its two heads crossing the knee joint, is particularly involved in generating power during the initial phase of the jump, while the soleus, which lies deeper and is more involved in activities like running and standing, contributes to the overall force output.
Amazing gym addition! I’ve been wanting a calf machine for my at home gym but have never been able to pull the trigger due to price. The Calf Buster is affordable, fits in any space, and actually works my calf muscles better than a traditional machine. 10/10 product for your gym!
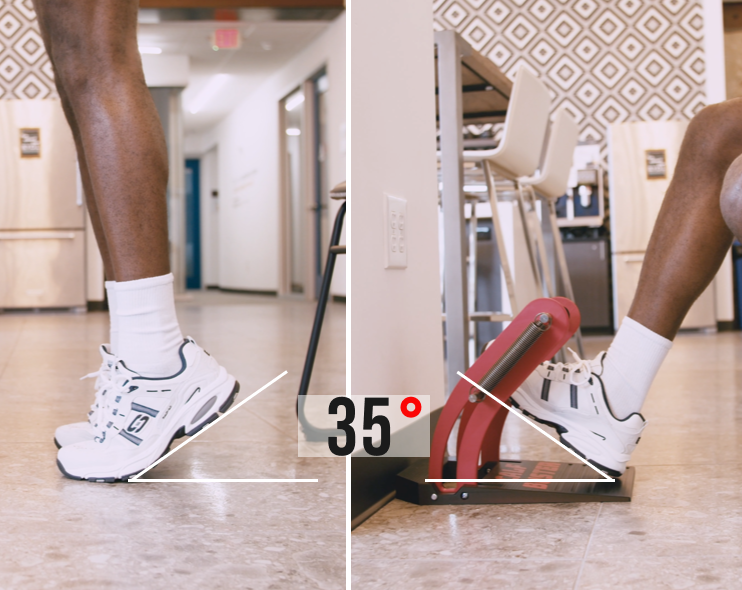

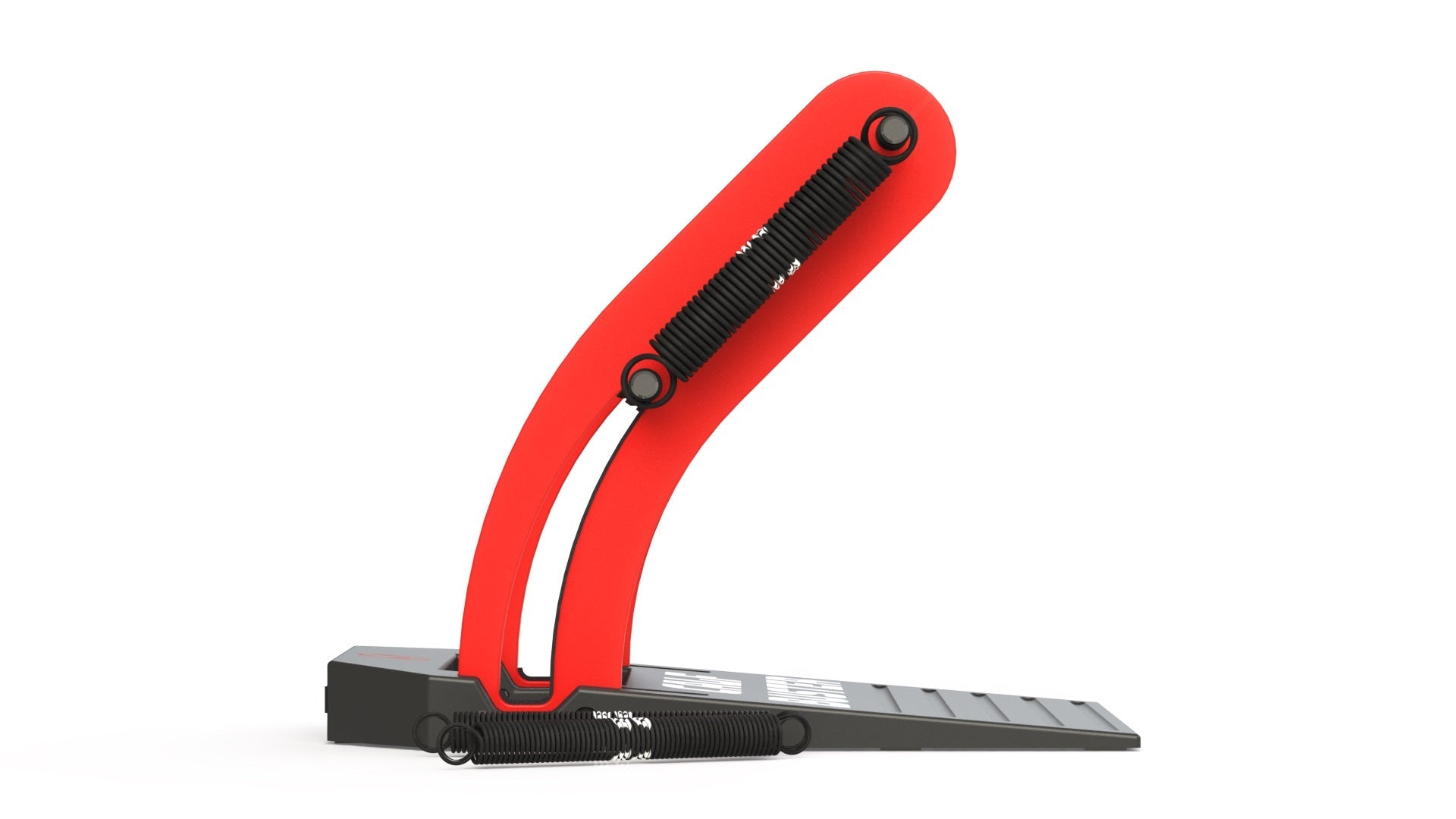
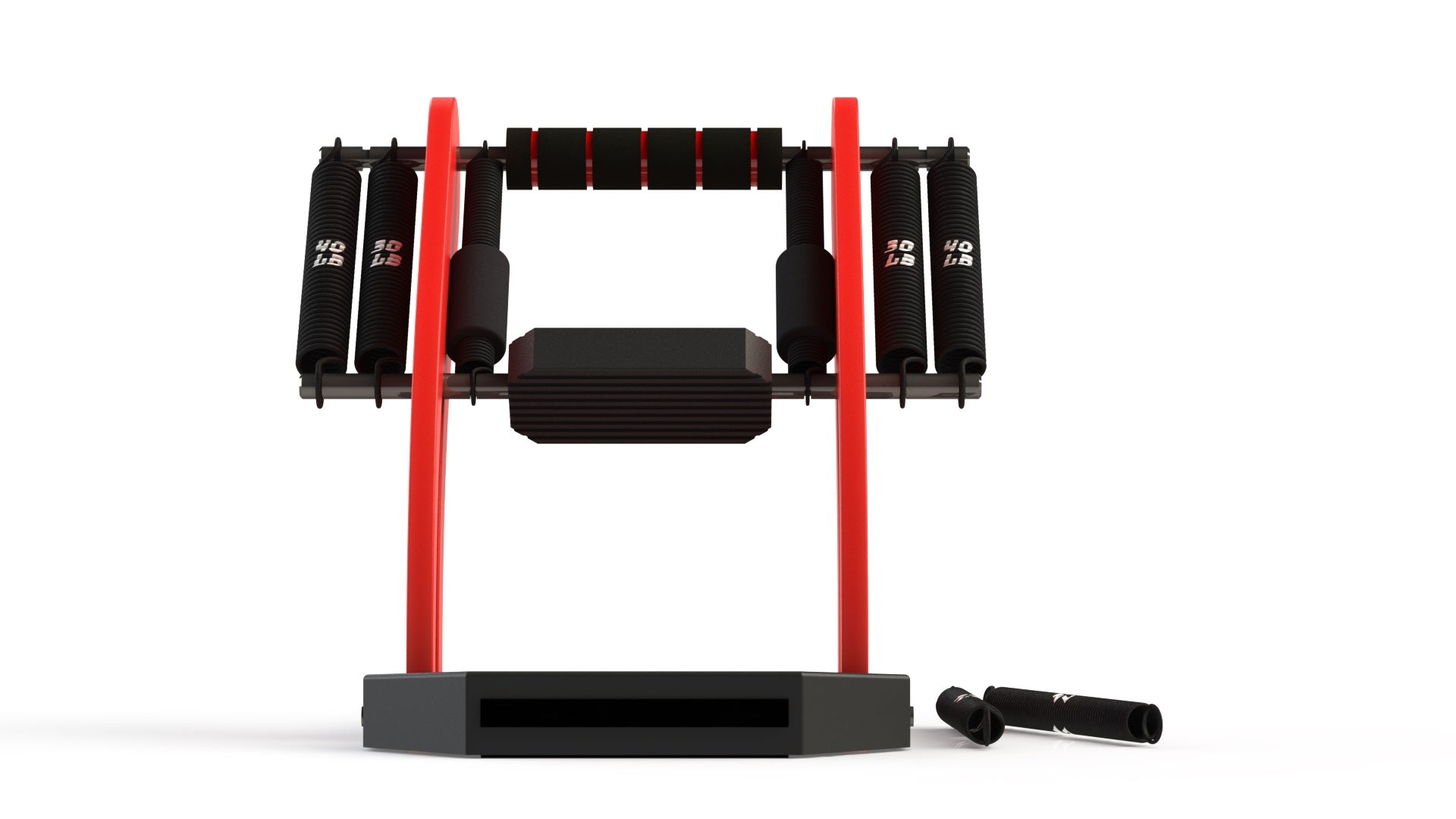
By providing 35 degrees of tensioned ankle rotation, the Calf Buster enables users to experience a deep muscle burn over the full range of their calf contractions. This extended range of motion allows for a more comprehensive activation of the calf muscles, including both the gastrocnemius and soleus. The gastrocnemius, located superficially and forming the visible bulge of the calf, is primarily involved in movements with a fully extended knee, such as jumping. On the other hand, the soleus, positioned deeper and responsible for maintaining posture and stability, is engaged during activities involving bent knees, like squat jumps.
The tensioned ankle rotation provided by the Calf Buster challenges the calf muscles throughout the entire range, making each repetition more demanding and effective. As the calf muscles contract, they experience tension and resistance that progressively increases as the ankle is rotated. This added resistance not only promotes muscle growth and strength development but also enhances the overall muscle engagement and intensity of the exercise.